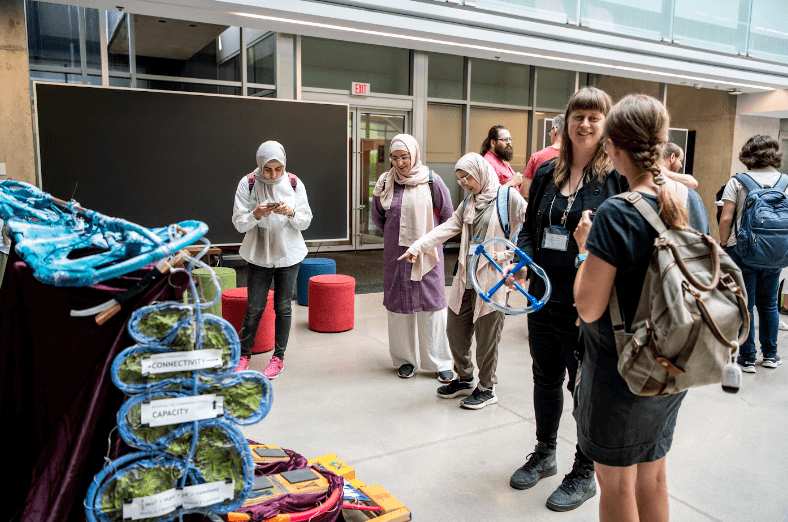
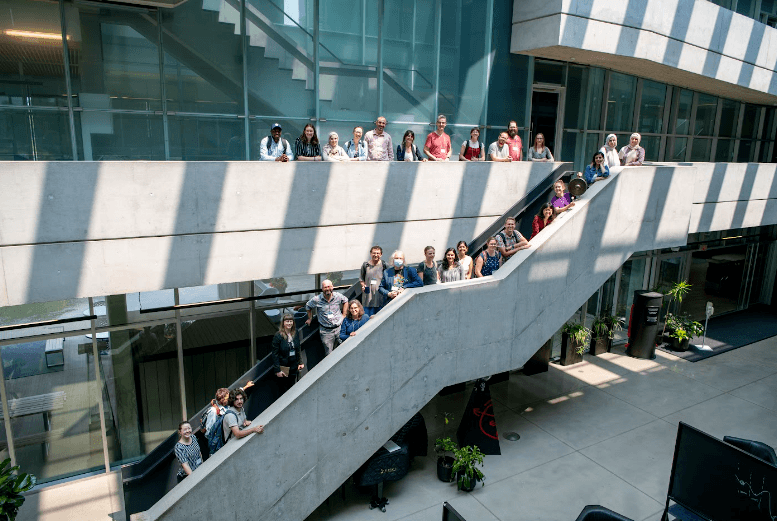
On July 17, the Perimeter Institute played host to the first Hammers & Nails climate workshop.
The new event was part of the emerging Math4Climate network in Canada and was a chance for researchers to interact with invited experts from diverse fields focused on climate, energy, and biodiversity.
How do hammers and nails relate to climate research?
The first half of the workshop was dedicated to short research pitches, where both Perimeter researchers as well as guests from the Math4Climate network (including Waterloo Institute for Complexity and Innovation, and the University of Waterloo’s Climate, Energy, and Water Institutes) could present their hammers and nails.
Hammers refers to methods used by Perimeter researchers in their daily work (causal inference, techniques in algebraic topology, strong gravity simulations, etc.). While nails refer to open challenges within climate, energy & biodiversity research.
The second half of the workshop built on these pitches through informal group discussions and was capped off with a delicious fully vegan lunch provided by the Black Hole Bistro.
A Curiosity-Based Approach
What sets this workshop apart is its curiosity-based approach to climate. “The aim was to get people from very diverse research backgrounds in the same room, thanks to their shared curiosity about climate-related research,” says Anna Knörr, a recent graduate of Perimeter's PSI master's program and one of the main organizers of the event.
“We are not claiming that quantum field theory methods will instantly solve climate change, it’s rather about asking new questions about climate by having unusual groupings of people talk to each other about these issues.”
If research directions do emerge from the event, then it could certainly come from "ways of thinking" that are unique to research at Perimeter.
Work with your hands
That unique way of thinking goes beyond concrete tools such as math and coding. It is the way researchers fundamentally approach a problem.
When tackling quantum field theory or quantum many-body systems, for example, theoretical physicists are often faced with a variety of complex problems. To help make tangible progress, researchers will often use toy models that represent a handful of phenomena to focus on.
This helps researchers gain a solid understanding of fundamental principles on which to ground their intuition for the actual system with all its complexities. Such ways of thinking can also be valuable for approaching complex questions related to climate, energy and society.
A first topic that PI's researchers may continue to explore in this regard, together with other workshop participants, are toy models for climate tipping points, from not only a geophysical but also a socio-financial perspective.
Continuing Momentum
The meeting itself was part of a series of climate-focused workshops that have sparked off each other thanks to the emerging Math4Climate network in Canada.
The network aims to bring mathematicians together with experts in climate, energy, and biodiversity to discuss challenges from a unique perspective. Most importantly, the initiative emphasizes that issues such as climate change cannot be addressed through purely technical solutions, but requires social change.
From the success of the first workshop, the goal is to continue these conversations into a series of lunches hosted by Perimeter’s Climate Working Group.
“We are trying to integrate climate awareness into the busy lives of Perimeter researchers,” says Anna “and we think a curiosity-driven approach is the way to make it happen.”
Further exploration
À propos de l’IP
L'Institut Périmètre est le plus grand centre de recherche en physique théorique au monde. Fondé en 1999, cet institut indépendant vise à favoriser les percées dans la compréhension fondamentale de notre univers, des plus infimes particules au cosmos tout entier. Les recherches effectuées à l’Institut Périmètre reposent sur l'idée que la science fondamentale fait progresser le savoir humain et catalyse l'innovation, et que la physique théorique d'aujourd'hui est la technologie de demain. Situé dans la région de Waterloo, cet établissement sans but lucratif met de l'avant un partenariat public-privé unique en son genre avec entre autres les gouvernements de l'Ontario et du Canada. Il facilite la recherche de pointe, forme la prochaine génération de pionniers de la science et communique le pouvoir de la physique grâce à des programmes primés d'éducation et de vulgarisation.
Ceci pourrait vous intéresser