Among other things, Perimeter researchers are working on quantum error correction (the techniques needed to safeguard and verify information amid the errors inherent to quantum computation), study quantum complexity (which attempts to classify computational problems by how difficult they are for a quantum computer to solve), and pursue the application of quantum information techniques and insights to other areas of physics, including quantum foundations and condensed matter.
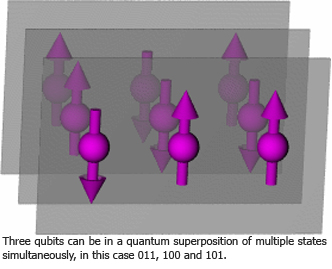
Quantum mechanics allow atoms to be in a quantum superposition. Superposition is a little like being in two places at one time. However, if you look at a quantum superposition, the particle has to decide where to be, and you can only ever see it in one of those two places.
Quantum information is the effort to both understand and use the properties of the quantum world.
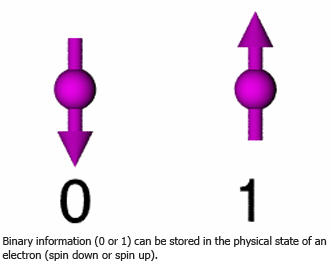
The memory of a regular computer consists of a sequence of bits representing some number (which in turn might represent a picture or words or anything else). The computer does computations by changing that number according to its program. If we can instead build a computer out of single atoms or other microscopic objects, the memory of the computer could instead be in a quantum superposition. The information stored in such a computer would be quantum information, composed of qubits (short for "quantum bit") instead of bits. A quantum computer could perform some computations much faster than any plausible classical computer.
The properties of qubits are sometimes very different from the properties of classical bits. Qubits cannot be copied to create multiple replicas. Another property of qubits is entangled states. They are special kinds of quantum states that allow two qubits to be more highly correlated than is possible for classical bits. These special properties allow other surprising applications of quantum mechanics. For instance, quantum cryptography allows more secure secret codes by taking advantage of the resistance of qubits to copying.
One major focus of quantum information researchers at Perimeter is to understand the properties of quantum information. Sometimes this takes the form of figuring out what new technologies quantum information can enable (such as new quantum cryptography protocols). Sometimes, we instead find limits on the power of quantum information (for instance, by discovering that certain computational problems are likely to be too hard for even a quantum computer to solve).
Sometimes we try to pinpoint the ways in which quantum systems are different from classical systems (by studying the distinction between quantum systems that can be easily simulated on a classical computer and those that cannot). And sometimes, we simply try to understand the strange behavior of quantum states with no particular application in mind (for instance, by studying the structure of complicated entangled states).
Actually building a quantum computer is a daunting task because of the challenges involved in manipulating individual atoms with high precision. Some of our associate faculty at the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) are engaged in experiments aimed at constructing quantum computers. At Perimeter, we do a good deal of theoretical work that can help in this long-term task. We study quantum error correction and fault-tolerant quantum computation to allow experimenters to more easily construct large quantum computers, without requiring that the individual components of the quantum computer be perfect. We also think about improved ways to measure the properties of quantum systems, particularly those which are to be used to build a quantum computer.
The deeper insight we are trying to develop into the properties of quantum states pays off in other areas of physics as well, since so many systems of interest to physicists are inherently quantum-mechanical. A number of Perimeter researchers have a shared interest in quantum information and condensed matter or quantum foundations, and have also pursued applications of quantum information ideas to particle physics, astronomy, string theory, and quantum gravity.